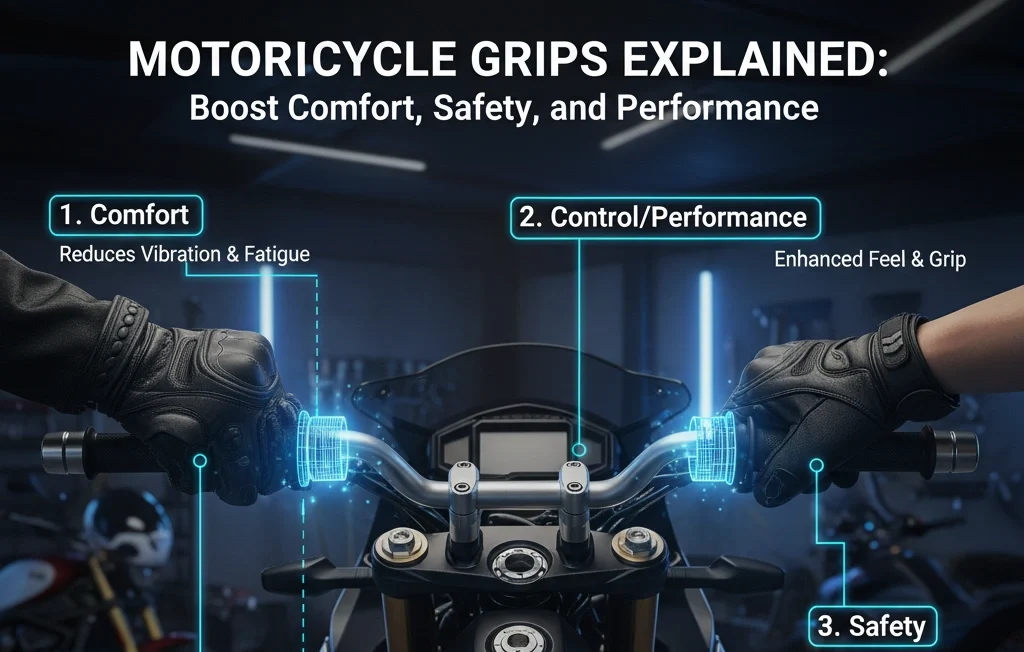
Each rider is directly in touch with their machine at the handlebars. The control interface of the main interface mainly consists of grips, which have an influence on throttle response, braking feel or operating grip in handling. They do not have to be rubber tubes; the correct ones can increase comfort, accuracy and riding duration.
Fatigue, loss of precision and slippage of hands are associated with worn or poor grip. This guide discusses the importance of motorcycle grips, the different kinds of grips, and demonstrates how the correct selection of grips may result in a tremendous change in your ride in terms of comfort, safety and the flavour of the ride.
What Are Motorcycle Grips and Their Significance?
Motorcycle grips, in simple terms, are basically referred to as the rubber or composite sleeves which are slipped on your handlebars. They have two tasks, to offer a secure and non-slipping surface and absorb these engine and road vibrations.
This may be simple to hear, but they play a significant role. They allow you to have control also under throttle, particularly when cornering, braking or even in wet weather. Typical issues related to the worn-out or inexpensive grips are:
- Slippery surfaces which make the hands slide.
- Shaky type: Transferring of vibration, and then becomes numb or tired.
- Front-end poor feedback, obstructing handling.
The grip is more than a matter of taste, but it is also an aspect of balancing your bike.
The role of Grips on Comfort, Safety and Performance
The choice of grip varies in all respects:
- Comfort: Damping grips to prevent high-frequency engine vibrations and low-frequency bumps of the road, so that you can ride longer with no pins and needles. Foam and gel materials are good for this.
- Safety: In case of emergency, a safe hold is all that is required. Non-slip textured handlebars will prevent your hands from sliding down the bars or loss of throttle control with sharp braking, or avoidance cuts or swerves. Your line of first defence is that.
- Performance: The appropriate diameter and texture enhance the handling precision of the riders who wish to take their performance to the next level. With a sport grip, you get instant feedback, whereas you are not affected by the shocks on the road with a touring grip.
Types of Motorcycle Grips
1-Rubber Grips
General and most popular. The contemporary rubber grips are strong, cheap and waterproof. Softer ones pick up less vibration, pick up more, and hard compounds have much longer life. Good at commuting and all weather.
2-Foam Grips
Foam grips are very light and delicate, and vibration-damping. They make a favourite of the long-distance traveller and the rider of a cruiser ( consider Suzuki Boulevard or Yamaha V-Star). The trade-off includes a quicker degradation during rainy seasons when it is in heavy rain, and it is necessary to be able to replenish it constantly.
3-Gel Grips
These are a combination of a rubber shell, combined with an internally embedded gel core, and this serves as a shock absorber. They are the final solution to the rider who has wrist tiredness, arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome. A little bit heavier, they provide outstanding comfort not only on bumpy roads but also on long distances.
4-Heated Grips
An innovation to 365-day riding on a national scale in the UK. They are electrically powered, which allows hands to be warm in cold weather, keeping them warm without feeling numb and stiff, affecting control. Most kits are based on a normal 12 editions and are common on tour and adventure bikes.
5-Performance Grips
Factory balanced to racetrack racing or loose road riding. They have braver texturing and are made thinner, and focus more on hard throttle feel and hard control instead of trim comfort.

The Selection of Motorcycle Grips
Choose the ideal grip as your ride style and requirements match one of them:
- Purpose: Touring? Choose foam or gel. Sport riding? Opt for performance grips. All‑whether commuting? Heated grips or rubber are most suitable.
- Dimensions and size: Ergonomics. An excessively thick grip produces fatigue, and one that is excessively thin produces diminished leverage. Riders with bigger hands use grips that tend to be slim, making them have a natural grip.
- Fittings: Check that he grip fits your model of motorcycle. The standard handlebar that is normally used is 7/8″, although the throttle tube side should always be checked to ensure the proper size.
How to Install Motorcycle Grips
Proper installation is critical towards performance and safety.
- Removal: Slide the old grip off under a squirt of a compression spray or with a spray of isopropyl alcohol under the old grip.
- Preparation: Clean up the handlebars and throttle tube, getting all the adhesive and residue off.
- Fitting: This is done by applying a piece of grip glue or hairspray (which is a lubricant which settles to its sticky state) so that the new grip will slide on.
- Safety Check: Make sure that the throttle tube is rotating when not attached and closing easily.
Maintenance and Replacement Guide
Check grips periodically in case of cracks, hardness or shiny spots. A hard or greasy grip has a safety risk and must be changed immediately. Wash them with soaps and do not use strong chemicals, as this may destroy the finishing.
Advantages of Replacing
Grip upgrades are among the least expensive upgrades.
Benefits are immediate:
- Radical accent on ride comfort and cutback vibration fatigue.
- Better throttle response, which is sharper and safer and much more reliable.
- An easy solution to renew the morphology of your motorcycle in a variety of colours and textures.
Conclusion
Your motorcycle grips are a trivial object with an immense influence. The direct physical connection to the motorcycle that determines the safety, comfort and performance of each journey. The right set will decrease fatigue, increase confidence and leave a person with an actual better riding experience.